An N-Channel MOSFET is made up of an N channel, which is a channel composed of a majority of electron current carriers. The gate terminals are made up of P material. Depending on the voltage quantity and type (negative or positive) determines how the transistor operates whether it turns on or off.
- The application of a negative (-ve) gate voltage to the p-type 'enhancement-mode' MOSFET enhances the channels conductivity turning it “ON”. In contrast, n-channel depletion-mode devices have a conductive channel naturally existing within the transistor.
- It is the maximum current in the tolerance range of drain-source voltages, V DS, that can be achieved. I DSS is referred to as the drain current for zero bias, because the gate-source voltage requires no bias voltage to operate. The gate-source voltage is just zero. No voltage needs to be applied to it.
- MOSFET Transistor is a special type of transistor that is used in various digital circuits and amplifying electronic signals. But if you ‘re in search of more application about the MOSFET transistor or want to gain more information about this post is for you.
- MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor or Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. This is also called as IGFET meaning Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor. The FET is operated in both depletion and enhancement modes of operation. The following figure shows how a practical MOSFET looks like. Construction of a MOSFET.
A N-Channel MOSFET is a type of MOSFET in which the channel of the MOSFET is composed of a majority of electrons as current carriers. When the MOSFET is activated and is on, the majority of the current flowing are electrons moving through the channel.
This is in contrast to the other type of MOSFET, which are P-Channel MOSFETs, in which the majority ofcurrent carriers are holes.
Before, we go over the construction of N-Channel MOSFETs, we must go over the 2 types that exist. There are 2 types of N-Channel MOSFETs, enhancement-type MOSFETs and depletion-type MOSFETs.
A depletion-type MOSFET is normally on (maximum current flows from drain to source) when no differencein voltage exists betweeen the gate and source terminals. However, if a voltage is applied to its gate lead, the drain-source channel becomes more resistive, until the gate voltage is so high, the transistor completely shuts off. An enhancement-type MOSFET is the opposite. It is normally off when the gate-source voltage is 0(VGS=0). However, if a voltage is applied to its gate lead, the drain-source channel becomesless resistive.
In this article, we will go over how both N-Channel enhancement-type and depletion-type are constructed and operate.

How N-Channel MOSFETs Are Constructed Internally

An N-Channel MOSFET is made up of an N channel, which is a channel composed of a majority of electron current carriers. The gate terminals are made up of P material. Depending on the voltage quantity and type (negative or positive)determines how the transistor operates whether it turns on or off.
How an N-Channel Enhancement type MOSFET Works
How to Turn on a N-Channel Enhancement type MOSFET

To turn on a N-Channel Enhancement-type MOSFET, apply a sufficient positive voltage VDD to the drain of the transistorand a sufficient positive voltage to the gate of the transistor. This will allow a current to flow through the drain-source channel.
So with a sufficient positive voltage, VDD, and sufficient positive voltage applied to the gate, the N-Channel Enhancement-type MOSFET is fully functional and is in the 'ON' operation.
How to Turn Off an N-Channel Enhancement type MOSFET
What Is Mosfet And Its Uses
To turn off an N-channel Enhancement MOSFET, there are 2 steps you can take. You can either cut off the bias positivevoltage, VDD, that powers the drain. Or you can turn off the positive voltagegoing to the gate of the transistor.

How a N-Channel Depletion-type MOSFET Works
Mosfet Explained
How to Turn on an N-Channel Depletion-Type MOSFET
To turn on an N-channel Depletion-type MOSFET, to allow for maximum current flow from drain to source, the gate voltage should be set to 0V. When the gate voltage is at 0V, the transistor conducts the maximum amount of current and is in the active ON region. To reducethe amount of current that flows from the drain to source, we apply a negative voltage to the gate of the MOSFET. As the negative voltage increases (gets more negative), less and less current conducts across from the drain to the source. Once the voltage at the gate reaches a certain point, all current ceases to flowfrom the drain to the source.
So with a sufficient positive voltage, VDD, and no voltage (0V) applied to the base, the N-channel JFET is in maximum operation and has the largest current. As we increase the negative voltage, current flows gets reduced until the voltage is so high (negative), that all current flow is stopped.
How to Turn Off an N-Channel Depletion-type MOSFET
To turn off the N-channel Depletion-type MOSFET, there are 2 steps you can take. You can either cut off the bias positivevoltage, VDD, that powers the drain. Or you can apply sufficient negative voltage to the gate. When sufficientvoltage is applied to the gate, the drain current is stopped.
Mosfet Meaning In Electronics Engineering
MOSFET transistors are used for both switching and amplifying applications. MOSFETs are perhaps the most popular transistors used today. Their high input impedance makes them draw very little input current, they are easy to make, can be made very small, and consume very little power.
Related Resources
How to Build an N-Channel MOSFET Switch Circuit
P Channel MOSFET Basics
N Channel JFET Basics
P Channel JFET Basics
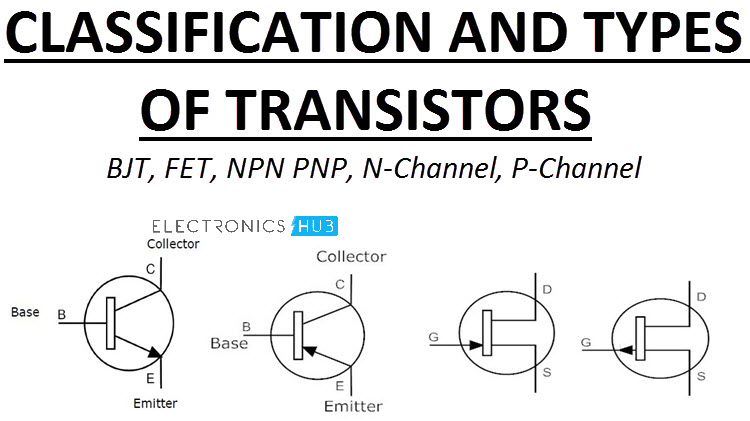
Types of Transistors
Mosfet Symbols
